Renewables
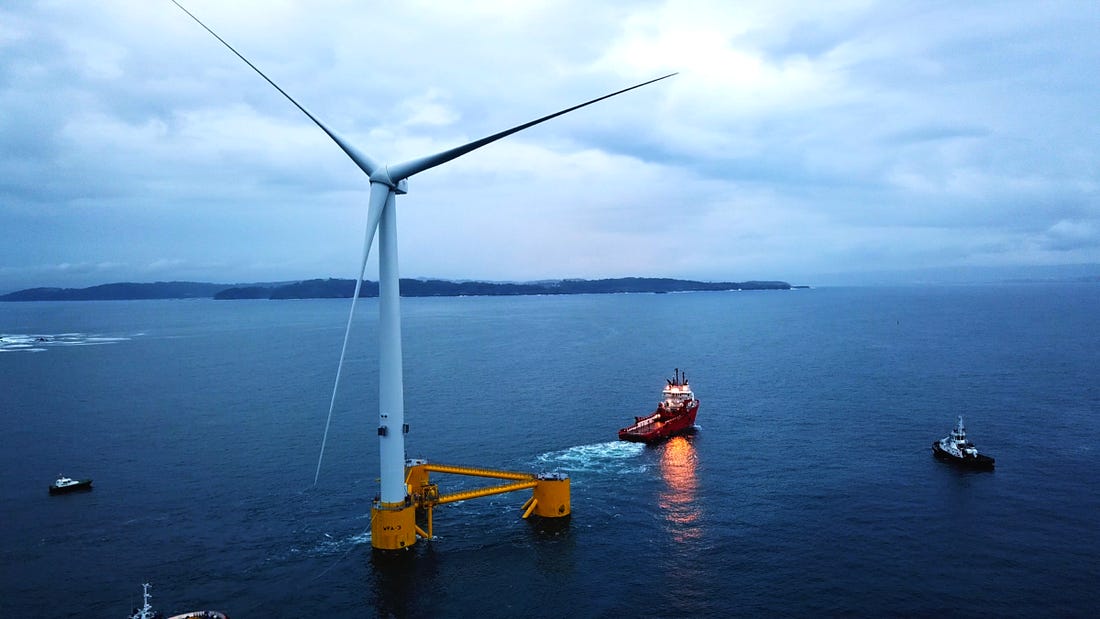
The International Energy Agency (IEA) have released their Offshore Wind Outlook 2019 Report which suggests offshore wind will become a $1 trillion industry.
The IEA finds that global offshore wind capacity may increase 15-fold and attract around $1 trillion of cumulative investment by 2040. This is driven by falling costs, supportive government policies and some remarkable technological progress, such as larger turbines and floating foundations. That’s just the start – the IEA report finds that offshore wind technology has the potential to grow far more strongly with stepped-up support from policy makers.
The largest and most powerful wind turbine to be used in a floating wind project – the V164-8.4 MW turbine from MHI Vestas – is now in place.
? Biology
CRISPR, the precision gene-editing tool, got a major upgrade last week that is being described as a true search-and-replace function for DNA. Traditional CRISPR works by cutting the DNA double helix and waiting for the cell to fix the mistakes, but this approach can lead to unpredictable changes in the DNA. The improved technique, called prime editing, can make insertions, deletions, and edits without breaking the DNA double helix which leads to greater efficiency and far lower risks of off-target editing.
David Liu, one of the Harvest University biologists behind prime editing, claims the new technique is capable of repairing almost all genetic diseases.
Why is that a big deal? Because with such fine-tuned command of the genetic code, prime editing could, according to Liu’s calculations, correct around 89 percent of the mutations that cause heritable human diseases. Working in human cell cultures, his lab has already used prime editors to fix the genetic glitches that cause sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and Tay-Sachs disease. Those are just three of more than 175 edits the group unveiled today in a scientific article published in the journal Nature.
Separately to this, a Russian biologist has started editing human eggs in order to correct a genetic defect that causes deafness, though he isn’t implanting any eggs until he gets regulatory approval. Getting approval isn’t guaranteed as the topic of creating gene-edited babies remains controversial in Russia and worldwide.
⚛️ Quantum Mechanics
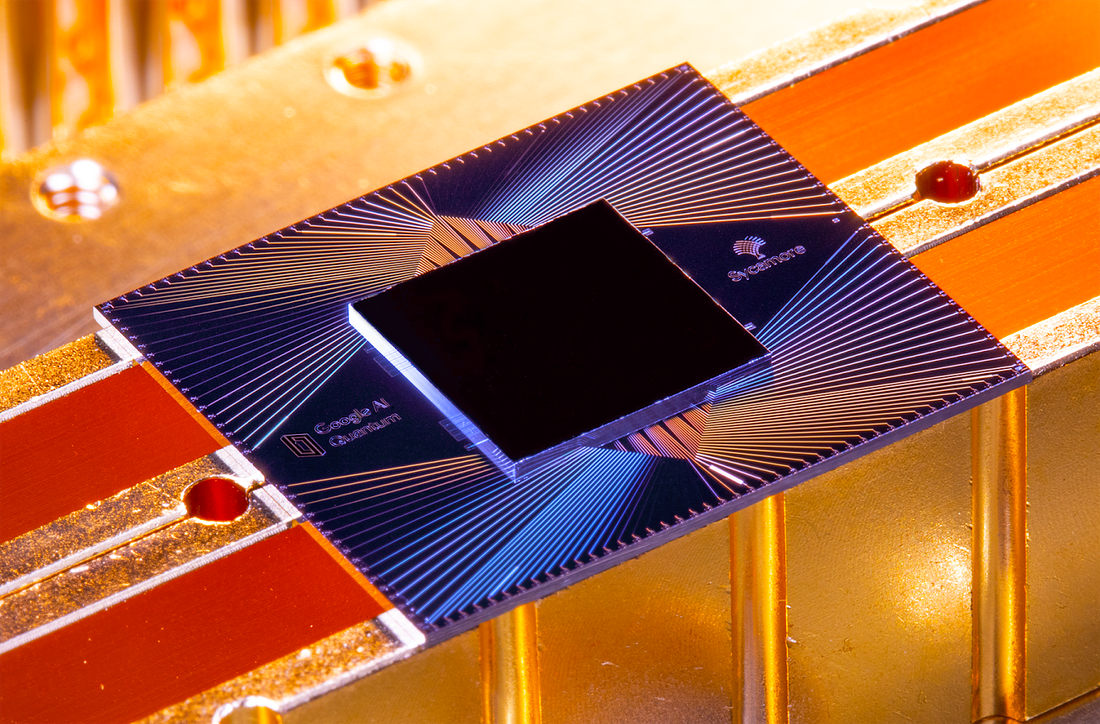
In a surprise to no one after the leaks last month, Google claimed to have achieved quantum supremacy with an article in Nature, a Google AI blog post, a Google blog post by CEO Sundar Pichai, and a slick 5-minute YouTube video.
Google AI developed a 53-qubit processor (“Sycamore”) which ran a specific computation that took 200 seconds to run. They estimate that the world’s fastest supercomputer would take 10,000 years to run the same computation, meaning that Google has achieved quantum supremacy.
IBM, which runs the world’s fastest supercomputer in the world (“Summit”), disputed the claim by saying that tweaking how Summit approached the task could reduce the computation time to 2.5 days — slower than 200 seconds, but still within the realms of “possible”, and thus not an achievement of quantum supremacy. Google responded by more or less saying “prove it”.
“We’re looking forward to when people actually run the idea on Summit and check it and check our data because that’s part of the scientific process – not just proposing it but actually running it and checking it,” said John Martinis. “At the same time, we’ll be making our quantum computers better.” We can’t be sure that IBM’s algorithm actually works until it is properly tested, he said.
If IBM’s claim is correct, it would downgrade Google’s claim from achieving quantum supremacy to achieving a quantum advantage, which would still be a significant landmark.
So, what does this all mean? Does it have any practical use today? Well, no… but it represents an important milestone in quantum computing. Google CEO Sundar Pichai describes it as follows in his blog post as follows:
For those of us working in science and technology, it’s the “hello world” moment we’ve been waiting for—the most meaningful milestone to date in the quest to make quantum computing a reality. But we have a long way to go between today’s lab experiments and tomorrow’s practical applications; it will be many years before we can implement a broader set of real-world applications.
We can think about today’s news in the context of building the first rocket that successfully left Earth’s gravity to touch the edge of space. At the time, some asked: Why go into space without getting anywhere useful? But it was a big first for science because it allowed humans to envision a totally different realm of travel … to the moon, to Mars, to galaxies beyond our own. It showed us what was possible and nudged the seemingly impossible into frame.
That’s what this milestone represents for the world of quantum computing: a moment of possibility.
What are those possibilities? Future applications will make use of quantum algorithms that are designed specifically to run on quantum circuits. The best known algorithms today are Shor’s algorithm, which will break classical cryptography, and Grover’s algorithm, which will vastly improve unstructured database search speeds.
? Artificial Intelligence
Google is improving 1 in 10 search queries by improving how it understands language context. The new approach applies BERT, one of Google’s natural language processing models, to both ranking and featured snippets in Search which should result in more relevant search results. Some examples are provided in their blog post.
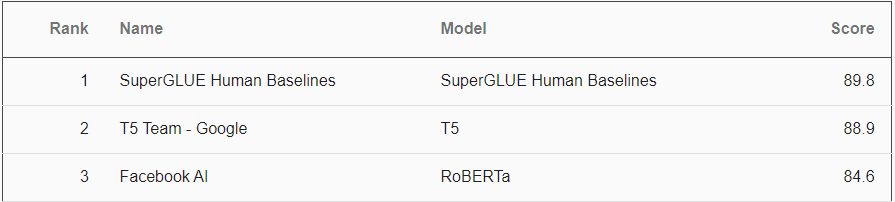
When language natural processing was discussed in Innovation Wrap #2, Facebook was at the top of the SuperGLUE leaderboard with its RoBERTa algorithm. Last week Google regained the top spot with its T5 (“Text-To-Text Transfer Transformer”) algorithm. The new algorithm achieved an overall score of 88.9, placing it just below the human baseline score of 89.8.
Improvements here should make their way into Google products over time, which will ultimately improve their service for both Google’s users and Google’s advertisers.
AI is being used to allow a paralysed person to “handwrite” with his mind.
An architect in New York believes AI will replace 90 percent of architect jobs as computers become better at automatically generating plans.
Deepfakes are being used by companies to dub their own videos into different languages.
?️ Space
SpaceX’s Starlink satellite broadband service will begin in 2020 and is currently being tested in US military planes. No pricing is available yet on their website.
Blue Origin, Jeff Bezos’s rocket company, has teamed up with three aerospace companies to enter a design for the next spacecraft to land American astronauts on the moon.
Bloomberg released a new 4-part series on YouTube called Giant Leap which gives a quick overview of the new business of space. Episode 1 looks at the new rocket launch companies, Episode 2 looks at space habitats, Episode 3 looks at manufacturing in space, and Episode 4 looks at asteroid mining and materials in space. Each episode runs for around 20 minutes.
? Gaming
Quartz writes that the birth of League of Legends proves how innovation can be a losing strategy. The article covers the beginnings of Riot Games’s League of Legends and how Blizzard failed to capitalise on this market with its previous games.
Twitch (Amazon) has lost another game streamer to Mixer (Microsoft) as Shroud joins Ninja on the platform.
? Chips and Computing
China has set up a new $29 billion semiconductor fund as part of a continued effort to become less dependent on US technology.
Intel thinks it can get back to its regular 2-year cycle of manufacturing updates starting in 2021. The cycle had slowed to 2.5 years over the past few years.
⚡ Other Snippets
Autonomous robo-taxi company Zoox has raised another $200m for development along with testing in Las Vegas.
TikTok is facing regulatory scrutiny in the US as Senators wonder whether the Chinese-owned app poses national security risks.
Fabric is a startup that just raised $110 million for automated micro-fulfillment centres.
Virtual reality is being used by financial planners to help people plan their retirement.
Facebook sold 180,000 Oculus Quests in Q3 2019 which is still pretty small.
Researchers have grown rabbit and cow muscle cells on edible gelatin scaffolds that mimic the texture and consistency of meat.
Lab-grown meat has the unexpected benefit of being able to create ethical zebra burgers and other exotic foods. Who knows, they might be tastier.
Scientists have trained rats to drive tiny cars. Apparently they find it relaxing.